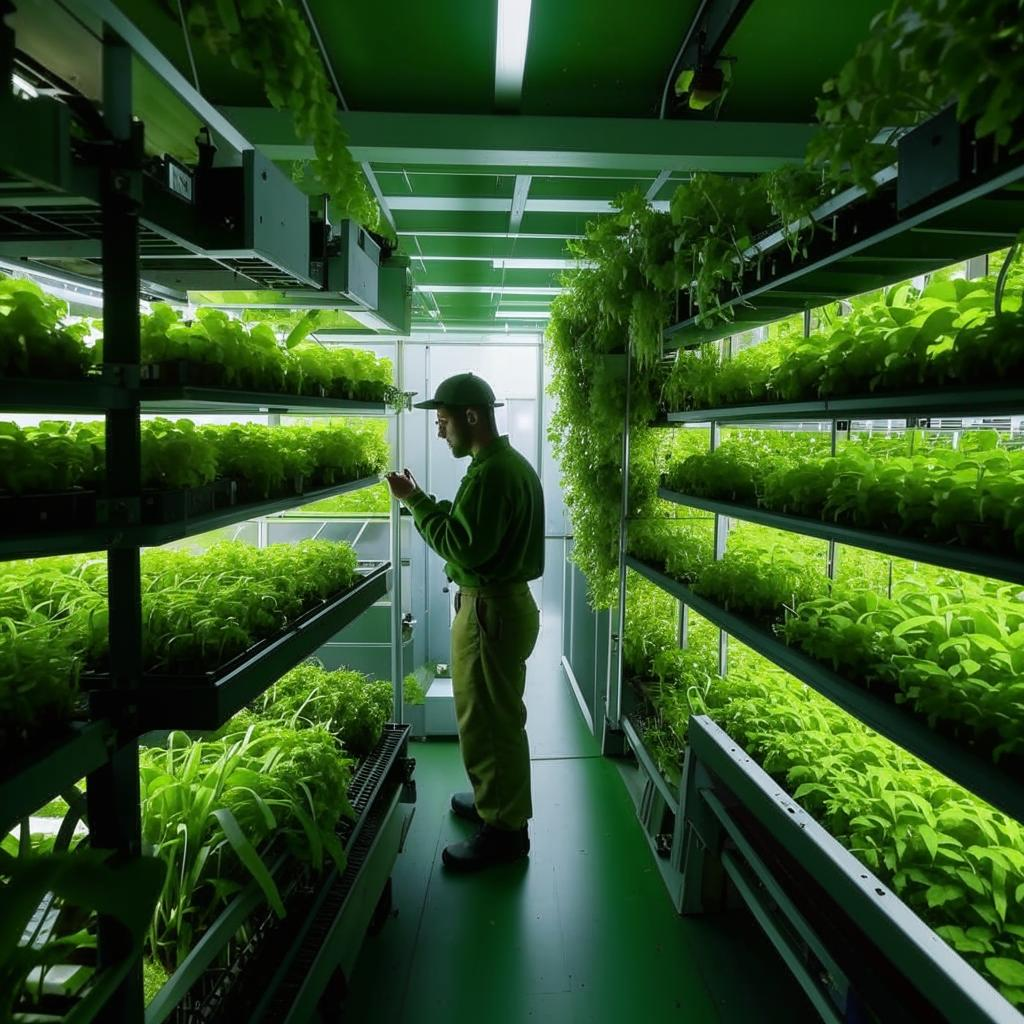
Vertical farming, an innovative approach to agriculture, is gaining traction as a solution to food security challenges posed by climate change. Traditional farming methods are increasingly vulnerable to droughts, floods, and extreme weather events, leading to crop failures and food shortages. Vertical farms, on the other hand, offer a controlled environment where crops can be grown year-round, regardless of external weather conditions.
These indoor farms utilize technologies such as hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics to cultivate plants without soil. LED lighting provides the necessary energy for photosynthesis, while water and nutrients are carefully regulated to optimize plant growth. This controlled environment allows for higher yields, reduced water consumption, and minimal use of pesticides and herbicides.
As climate change intensifies and traditional agricultural regions face increasing environmental pressures, vertical farming emerges as a promising alternative. By bringing food production closer to urban centers, it can also reduce transportation costs and carbon emissions associated with long-distance food supply chains. Furthermore, it opens opportunities for creating new jobs in urban areas and contributing to a more resilient and sustainable food system. Vertical farms represent a significant step towards addressing the growing global demand for food in a changing world.